Diffusion bonding / Thermo-compression bonding
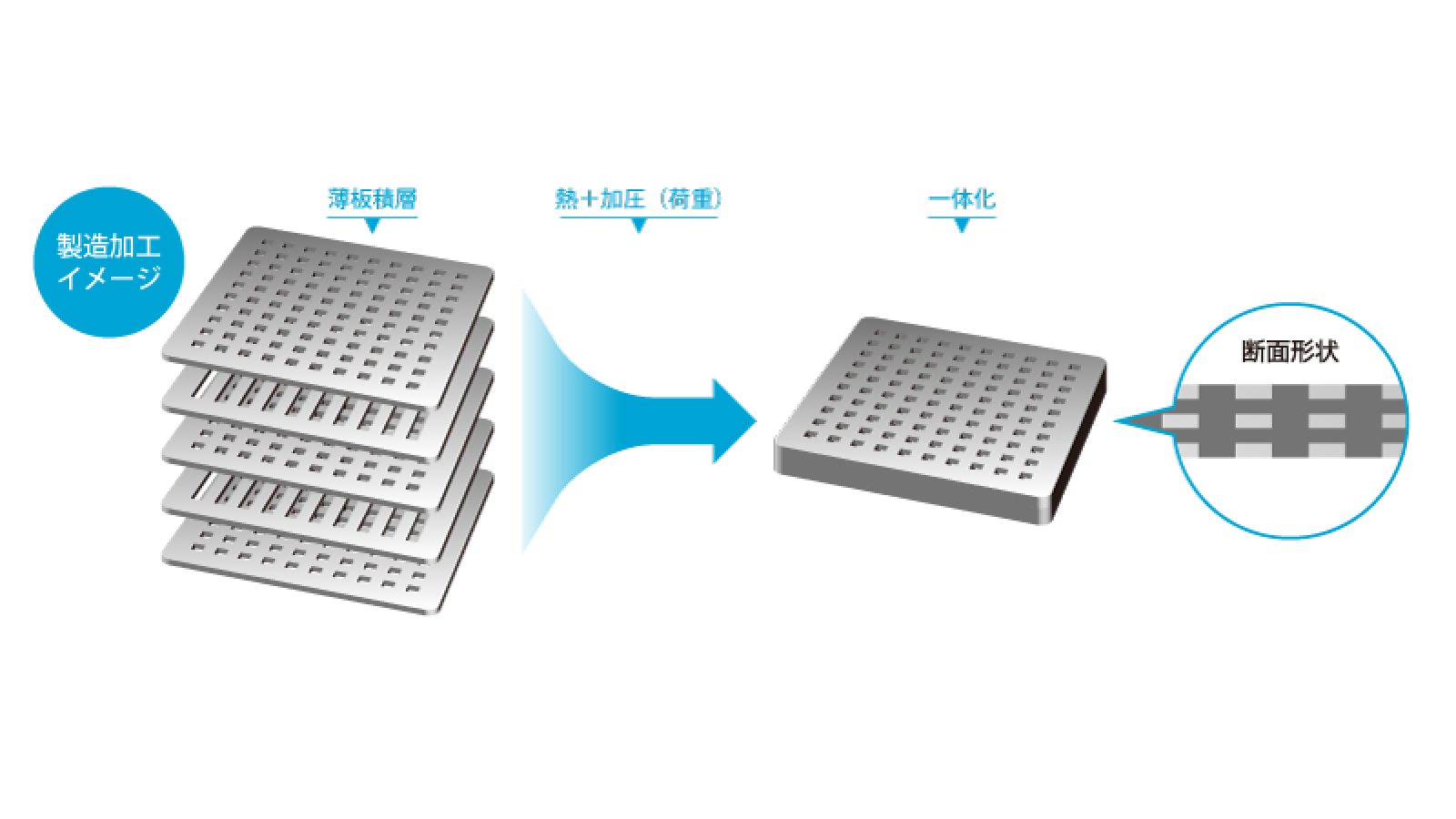
Although the etching process itself can be used with thin plates only, thicker products can also be manufactured by stacking and joining processed thin plates using diffusion bonding or thermo-compression bonding methods (base angle of 90 degrees (right angle) is also available) . Metals are usually joined together by adhesive or spot welding, but these methods have a number of drawbacks. Such bonds peel off at high temperatures, are difficult to clean, and spot welding creates gaps. To solve these problems, we recommend our proprietary thermo-compression bonding method.
Advantages of diffusion bonding
High strength and small dimensional changes due to lamination of thin plates
Clean and problem-free finish with gas generation and cleaning of protruding parts
Mass-production allows cost savings
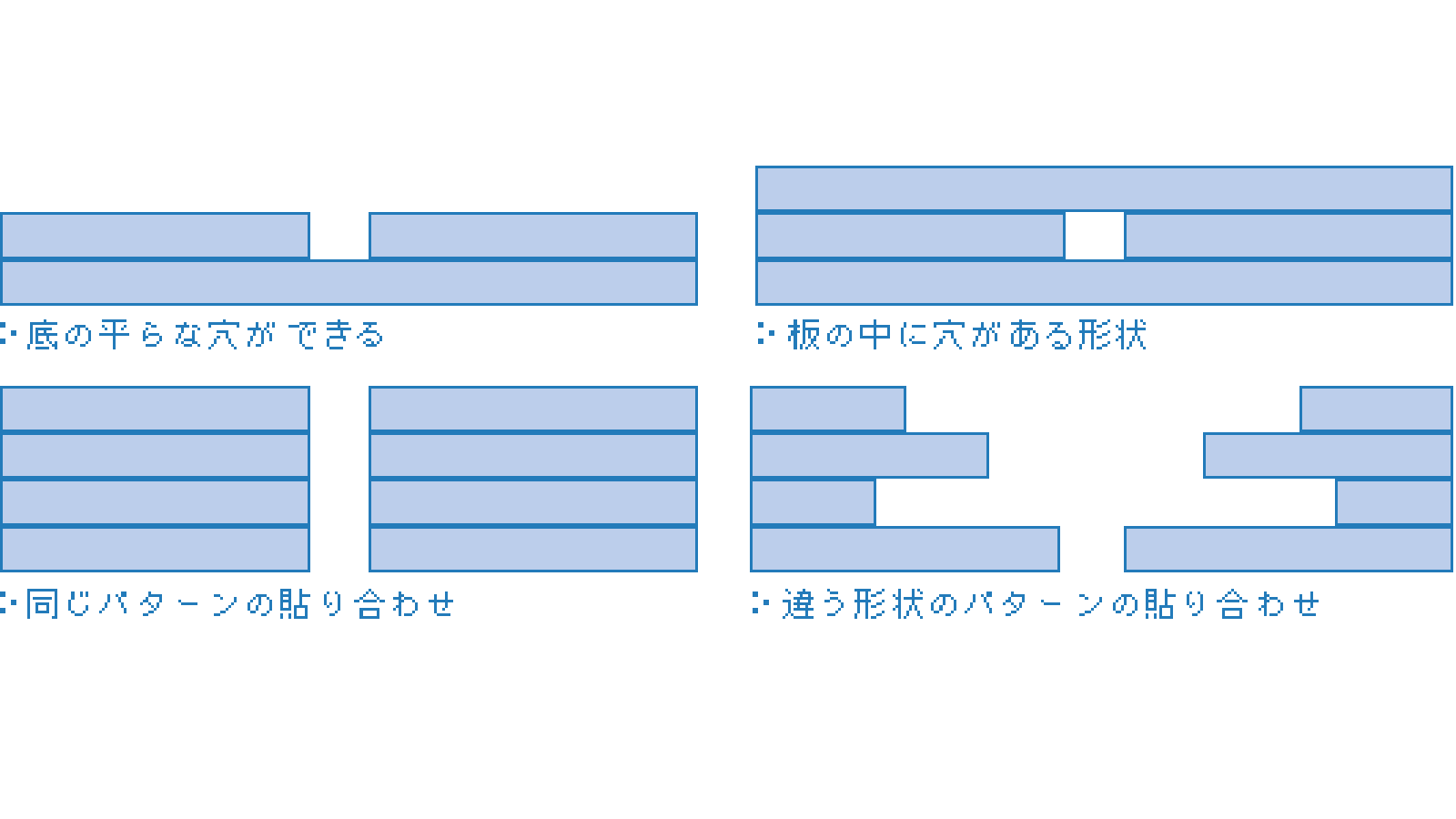
Deep holes, tapered holes and other complex shapes and channel structures are possible.
Manufacturing process image
Joint cross-section
Joinable materials
Stainless steel + stainless steel
Examples: SUS304+SUS304 SUS430+SUS430
42 alloy + 42 alloy
Invar + invar
Titan + titan
Copper + copper
We also can handle other materials, so please consult as.
Number of joined plates and thickness
Possible sizes vary depending on the plate thickness and shape, so please contact us for more information.
Joining application examples
Fuel cell separators
Deposition masks
Suction plates
Carrier tape
Semiconductor manufacturing jigs
Electronics components
Various filters
Heat exchanger parts
Fuel cell parts
Wire bonders
Heat sinks, etc.
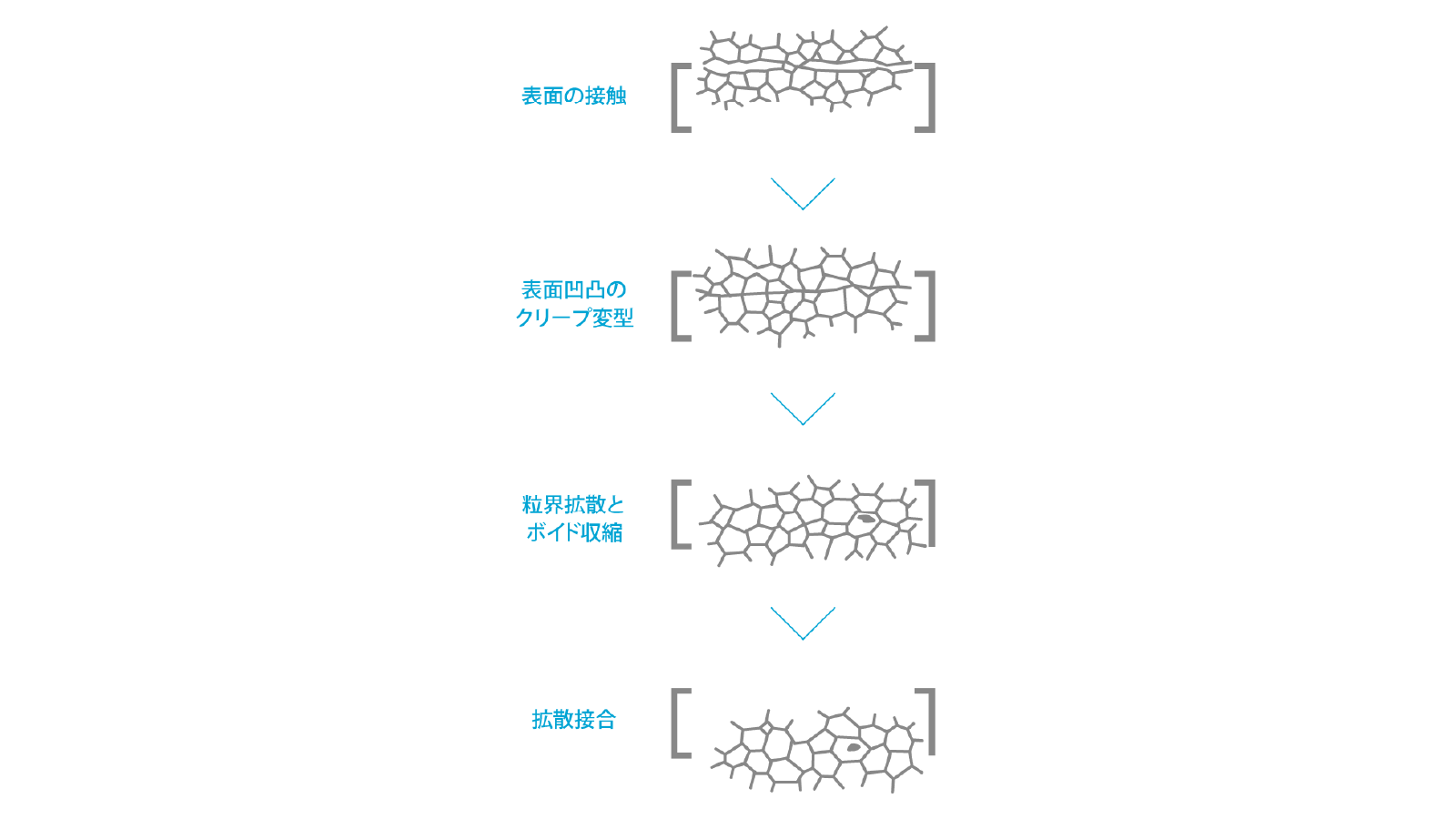
Principle of diffusion bonding
A metal bond is formed when two metal surfaces are brought close to each other at an atomic level. Therefore, joining is theoretically possible by bringing two metals close together.
Diffusion bonding is a process based on this principle. In it two metal surfaces are metallurgically bound in a solid state using heat and pressure.